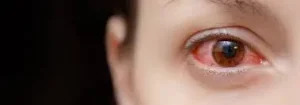
Uveitis also known as inflammation inside the eye occurs inside the eye. This is a very serious eye condition whereby the inflammation affects the uvea, which is in the middle layer of the eye. The uvea is made up of the iris, choroid, and ciliary body; all these parts have very vital roles in maintaining the health of the eye and vision. The primary symptoms of uveitis are pain, blurry vision, redness, and photophobia. It can affect any person of any age, though it is more typical in adults, mainly in the age group of 20-60 years. Any complications can be prevented if diagnosed at an early stage and treated well, thus saving your vision.
What is Uveitis?
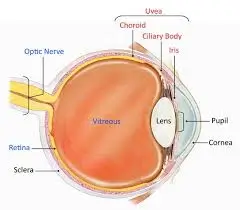 Uveitis is an inflammatory process affecting the uvea. The diversity of location and extent of inflammation allows types to be distinguished. Anterior uveitis is the most common form of uveitis. Inflammation in this is located in the anterior part of the uvea and predominantly involves the iris.
Uveitis is an inflammatory process affecting the uvea. The diversity of location and extent of inflammation allows types to be distinguished. Anterior uveitis is the most common form of uveitis. Inflammation in this is located in the anterior part of the uvea and predominantly involves the iris.
Intermediate uveitis
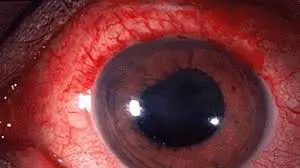
The ciliary body, located between the iris and choroid, becomes inflamed in this variant.
Posterior Uveitis:
This involves inflammation of the choroid in the back of the uvea and it may also irritate the retina.
Panuveitis
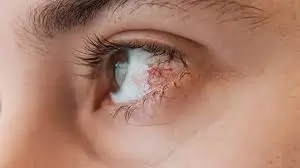
This is a more serious form in which the inflammation takes place in all parts of the uvea.
Uveitis Causes
The uveitis causes vary and range from an infection to autoimmune disorders. Some of the common causes are:
Infections

The bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites can cause uveitis. Common infectious causes include herpes simplex virus, tuberculosis, syphilis, and toxoplasmosis.
Autoimmune Disorders
Disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and sarcoidosis are among the causes of uveitis because the immune system mistakes the tissues of the eye and attacks them.
Injury
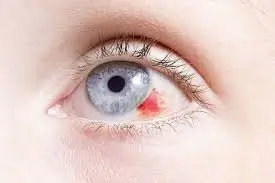
Other than biological causes, blunt force trauma or chemical exposure to the eye is also one of the reasons for inflammation in the uvea.
Stress

Some cases of uveitis have also been linked to psychological stress; this may trigger or worsen the condition in people who are prone to it.
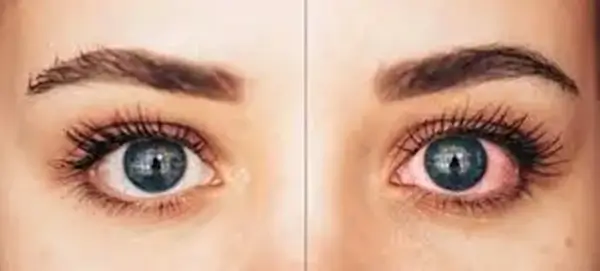
Uveitis Symptoms
The uveitis symptoms often come on suddenly and may involve one or both eyes. The most common signs include:
Reddening of the Eyes
The whites of one’s eyes usually turn red, which is a prevalent symptom.
Pain
Pain or sharp, aching sensation in the eye, usually with a one-sided headache, which can be a sign of uveitis.
Blurred Vision
The lack of clear focus in the eyes can present blurry vision, which could be a result of inflammation.
Sensitivity to Light
Photophobia Bright lights become unbearable and cause pain or discomfort.
Floating Spots
Small spots or shapes floating in your field of vision can be a sign of inflammation.
Uveitis Treatment
Early and appropriate uveitis treatment helps in management and prevents further complications. The mode of treatment depends upon the cause of the problem and the acuteness of inflammation. It commonly includes:
Oral Medications
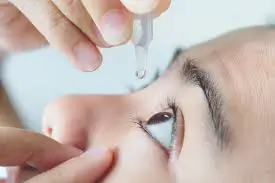
In more severe cases, if the usage of eye drops alone is not sufficient, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs can be prescribed to bring the inflammation under control.
Antibiotics or Antivirals
If an infection is the cause of uveitis, then appropriate antibiotics or antivirals will be prescribed to combat an underlying infection.
Surgery

If complications of uveitis occur, such as glaucoma or cataracts, then surgery may be necessary.
Prevention of Uveitis
While it is not possible to always prevent the problem of uveitis, some factors can minimize the risk of getting the problem:
Control Cases of Autoimmune Disorder
If one is suffering from an autoimmune disorder, one should get proper treatment for the disorder and keep it under control. It can help reduce the chances of getting uveitis.
Safe Eyes
Wear protective eyewear when participating in activities that may cause eye injury, including sports or chemical use.
Conclusion
Uveitis or the inflammation inside the eye is itself a serious issue that has to be attended to with concern and treated properly by adequate medical care to avoid long-term damage to vision. Early recognition of symptoms and the causes provide knowledge for seeking appropriate treatment. In case of any symptoms, the condition should immediately be brought to the attention of a specialist at Dr. Jawahar Lal Rohatgi Smarak Netra Chikitsalaya for proper care and management.




 Call Us Now
Call Us Now
Leave a Reply